Why You Should Do a Gut Microbiome Test
2860
Testing your gut microbiome helps you understand its functions and ensure it keeps you healthy and does not make you sick.

What is the Gut Microbiome?
A biome is a unique ecosystem defined by its environment and inhabitants. Within your intestines, your gut is a miniature biome teeming with trillions of microorganisms, including over 1,000 species of bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites.
Your gut microbiome is distinct to you. Infants acquire initial gut microbes through vaginal delivery or breastfeeding. As you grow, your diet and environmental exposures introduce new microbes to your gut, although some factors can also negatively impact and reduce your microbiota.
What does it do?
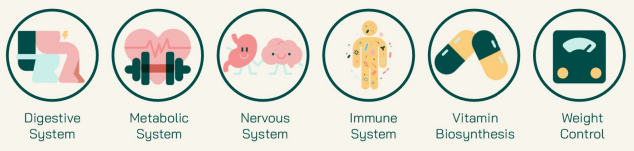
Your gut microbiome interacts with various body systems and supports numerous functions, functioning so actively that some healthcare providers liken it to an organ. While some interactions are still being studied, many are already well understood.
1. Digestive system
Gut bacteria aid in breaking down complex carbohydrates and dietary fibers that your body can’t digest alone. They produce short-chain fatty acids and essential nutrients, and supply enzymes needed to synthesize vitamins like B1, B9, B12, and K.
Gut bacteria help metabolize bile from the liver, breaking it down for reabsorption and recycling. Bile acids can't be recycled if this process fails, leading to fat digestion issues and cholesterol buildup in the blood.
2. Immune system
Beneficial gut microbes train your immune system to distinguish them from harmful pathogens. Your gut, which houses up to 80% of your immune cells, helps clear pathogens daily. These microbes also compete with harmful ones for resources and space, reducing the risk of infections like C. difficile and H. pylori.
Short-chain fatty acids from helpful bacteria support your immune system by maintaining the gut barrier, preventing bacterial toxins from entering the bloodstream and reducing inflammation. They may help suppress chronic inflammation linked to autoimmune diseases and other conditions.
3. Nervous system
Gut microbes influence your nervous system via the gut-brain axis, affecting neurotransmitter production, including serotonin. Short-chain fatty acids have positive effects, while bacterial toxins may harm nerves. Research is ongoing into how the gut microbiome impacts neurological, behavioral, and mood disorders.
4. Endocrine system
Gut microbes interact with enteroendocrine cells in your gut lining, which regulate metabolism, blood sugar, hunger, and satiety. Researchers are studying how the gut microbiome may influence metabolic syndrome, obesity, insulin resistance, and liver fat storage, though the exact relationships remain unclear.
Gut Microbiome Test and Screening in Bangkok, Phuket, Pattaya, Chiang Mai (Thailand)
Are You Having
✅ Abdominal bloating, frequent diarrhea, or persistent constipation?
✅ Ongoing inflammatory acne?
✅ Recurring allergic skin rashes?
✅ Issues with obesity and diabetes?
✅ Issues with chronic fatigue?
✅ Depression, anxiety or mood disorder?
Book your appointment today!
Contact us at info.bkk@pulse-clinic.com or chat on your preferred platform:
![]() +66 65 237 1936
+66 65 237 1936  @PULSEClinic
@PULSEClinic ![]() PulseClinic
PulseClinic
Trust PULSE CLINIC to take care of your health like other 45000 people from over 130 countries. We provide discreet professional service with high privacy. Here to help, not to judge.
Why You Should Do a Gut Microbiome Test
Though we’ve only begun to scratch the surface of understanding how the gut microbiome impacts health, there is already strong evidence linking gut health to the following areas:
1. Diabetes & obesity
Research shows a connection between the gut microbiome and metabolic disorders like insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and obesity. People with these conditions often have a reduced ability to produce beneficial substances from bacterial fiber digestion, such as butyrate and indole-propionic acid, and an increased production of branched-chain amino acids. Diet interventions, such as increased fiber, have improved blood glucose regulation in type 2 diabetes patients. Additionally, the drug Metformin is known to beneficially alter the gut microbiome.
2. Anxiety & depression
The gut microbiome has been associated with mental conditions like anxiety and depression. Research is ongoing to understand its role, but we know that the gut and brain communicate bi-directionally. Some gut bacteria produce or consume neurotransmitters such as GABA, norepinephrine, and dopamine, and certain bacterial substances may boost serotonin production in the gut. The full impact of these interactions on mental health is still being explored, so this is a field to watch closely.
3. Cardiovascular disease
The link between the gut microbiome and cardiovascular diseases is strengthening. Conditions like hypertension and atherosclerosis are now associated with a higher production of pro-inflammatory substances, such as trimethylamine-n-oxide and hexa-acylated lipopolysaccharides.
4. Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis were among the first diseases linked to the gut microbiome and are well-studied. Common findings in people with IBD include reduced bacterial diversity, lower gene potential for producing beneficial short-chain fatty acids like butyrate and acetate, diminished fiber breakdown, and increased production of hexa-acylated lipopolysaccharides. Researchers are exploring whether targeting the gut microbiome could help prevent and treat IBD.
5. Sports Nutrition
Scientists are now exploring how exercise affects the gut microbiome and whether the gut microbiome influences athletic performance. Preliminary studies suggest that regular exercise can boost the production of beneficial short-chain fatty acids by the gut microbiome. Additionally, research has found that marathon runners have a higher abundance of a bacterial species that converts lactic acid into propionate, a short-chain fatty acid that helps stabilize blood sugar levels.
6. More
The impact of the gut microbiome on our health is an evolving field with discoveries emerging regularly. For the latest insights, check out current scientific literature.
Gut Microbiome Test
The Gut Microbiome Test thoroughly analyzes the trillions of microorganisms in your gut. By examining a stool sample, it identifies the types and quantities of microbes, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microorganisms. The results offer valuable insights into your gut health, highlighting imbalances that could impact your digestion, immunity, and overall well-being.
Gut Microbiome Test Collection Process
The process of collecting a gut microbiome sample typically involves taking a stool (fecal) sample. This is because the gut microbiome is composed of microorganisms that are found in the digestive system, especially in the large intestine. Here's a general step-by-step overview of the collection process:
1. Preparation
- Avoid Certain Foods/Medications: Avoid certain foods, antibiotics, probiotics, or other medications for a few days before the test to ensure the accuracy of the results.
- Gather Supplies: The testing kit will generally include a sterile collection container, spatula or scoop for collecting the stool, gloves, and instructions.
2. Collection
- Use a Clean Toilet Seat or Container: Use a clean toilet seat, or you may be provided with a disposable liner or collection tray to place over the toilet to catch the stool. This helps avoid contamination.
- Collect Stool Sample: Use the provided spatula or scoop to collect a small amount of stool from different areas of the sample (e.g., top, middle, and bottom) to ensure a diverse representation of the microbiome.
- Place the Sample in the Collection Container: After collecting the sample, place it in the sterile container provided in the kit. Be sure to follow the instructions regarding how much to collect.
3. Sealing and Labeling
- Once the stool is in the container, securely close the lid to avoid leaks or contamination.
- Label the sample with your identification (if required) as instructed.
4. Testing Process
- The sample will be analyzed for the diversity and composition of the microbial species present in the gut. The lab may use various methods, like DNA sequencing, to identify different bacteria, fungi, and other microbes.
Tips for Accurate Results:
- Follow Instructions: It’s important to follow the specific instructions given with your test kit to avoid any contamination or issues with the sample.
- Timing: Some tests may request that the sample is taken at a specific time of day or under certain conditions, so be mindful of these details.
- Hygiene: Ensure that your hands and any utensils used are clean to avoid contaminating the sample.
Benefits to People With
Screening is recommended for individuals displaying symptoms that may suggest an imbalance in gut microbiota, including:
- Digestive issues such as bloating, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or constipation
- Frequent migraines or sleep disturbances
- persistent acne
- Recurring allergic skin rashes
- Asthma
- Metabolic dysfunction
- Risk factors associated with anxiety, depression, obesity, type 2 diabetes, and Alzheimer’s disease
- Chronic bad breath
- Mucus in stools
- Long-term antibiotic use
- Carbohydrate intolerance
- Chronic fatigue
- Regular use of antacids
- persistent nasal congestion
Patients with five or more symptoms may have an imbalance in their gut microbiota.
Full Panel Gut Microbiome Test at PULSE Clinic Thailand
NOTES:
1. Preparing for screening: Non-fasting screening from liquids or solids before screening, and Stop taking antibiotics for 3 days before screening.
2. PULSExpress service: Fuss-free service without consulting the doctors. Poo and the results will deliver to you.
Book your appointment today!
Contact us at info.bkk@pulse-clinic.com or chat on your preferred platform:
Trust PULSE CLINIC to take care of your health like other 45000 people from over 130 countries. We provide discreet professional service with high privacy. Here to help, not to judge.
Loading...
Clinic Locations
Loading...