Varicella-Zoster Virus (VZV)
4551
The Varicella zoster virus, identified as human herpesvirus 3, is among the nine herpes viruses documented to affect human
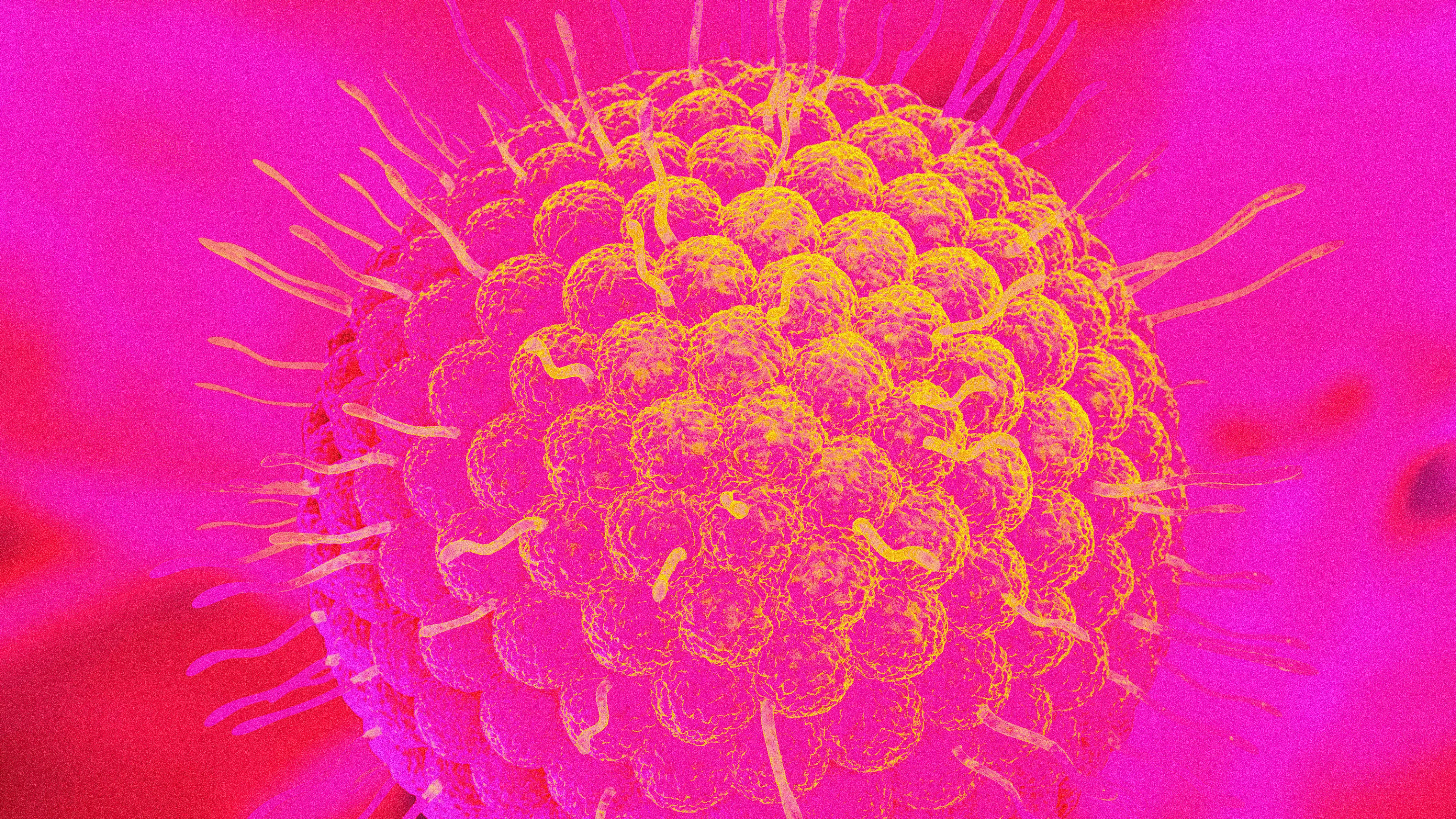
Overview of Varicella-Zoster Virus (VZV)
Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) is a herpes virus that causes chickenpox (varicella) and shingles (herpes zoster). It is highly contagious, primarily transmitted through direct contact or inhalation of aerosols from vesicular fluid. VZV establishes latency in sensory neurons and can reactivate later in life, leading to shingles. Vaccination and antiviral medications are available for the prevention and treatment of VZV infections.
Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) is a human herpesvirus that belongs to the alphaherpesvirus subfamily. It is one of nine known herpes viruses that can infect humans. VZV is the causative agent of two distinct clinical conditions: chickenpox (varicella) and shingles (herpes zoster).
Chickenpox, primarily affecting children and young adults, is characterized by a widespread rash of itchy vesicles (blisters) on the skin.
Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) establishes latency in sensory neurons after the primary infection, and later reactivates to cause shingles. Shingles are characterized by a painful rash with blisters that follow a specific distribution on one side of the body.
Persistent pain from shingles can result in postherpetic neuralgia. VZV is specific to humans and can survive in the environment quickly. It can also infect the central nervous system, leading to complications such as meningitis, encephalitis, and myelitis. In rare cases, VZV infection during pregnancy can cause severe fetal damage.
Get Tested and Treated for Varicella-Zoster Virus (VZV) at PULSE Clinic
Contact us at info.bkk@pulse-clinic.com or chat on your preferred platform:
![]() +66 65 237 1936
+66 65 237 1936  @PULSEClinic
@PULSEClinic ![]() PulseClinic
PulseClinic
What is the incubation period?
The virus enters the body through the respiratory system and has an incubation period of 10–21 days. Infected individuals become contagious 1-2 days before the appearance of skin lesions. Chickenpox is highly contagious and can spread through direct contact or inhalation of aerosols from the vesicular fluid.
What are the symptoms and complications of VZV?
VZV is not considered a sexually transmitted disease. Although the virus can be transmitted through direct contact with active shingles lesions, it does not cause genital herpes. However, the virus that causes genital herpes is another herpesvirus known as the herpes simplex virus (HSV), specifically HSV-2.
Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) can cause various symptoms and complications, depending on the specific condition it causes.
Here are the symptoms and complications associated with VZV infections:
Chickenpox (Varicella)
Symptoms of chickenpox (Varicella):
- Rash: The hallmark symptom of chickenpox is a rash that starts with red spots and progresses to itchy blisters. The rash typically appears on the face, scalp, trunk, and extremities.
- Fever: Many individuals with chickenpox experience mild to moderate fever.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired or fatigued is common during an illness.
- Headache: Some individuals may experience headaches.
- Bodyaches: Muscle and body aches can occur, similar to those experienced with the flu.
- Loss of Appetite: Chickenpox can cause a temporary loss of appetite.
- Mild respiratory symptoms: Individuals may sometimes experience a soft cough or runny nose.
The complications of chickenpox can include:
- Bacterial Infections: The blisters caused by chickenpox can become infected with bacteria, leading to skin infections.
- Pneumonia: In rare cases, chickenpox can lead to pneumonia, particularly in adults or individuals with weakened immune systems.
- Encephalitis: Although rare, chickenpox can result in brain inflammation (encephalitis), leading to neurological symptoms.
- Reye's Syndrome: Reye's syndrome, although extremely rare, is a severe condition that can occur in children who take aspirin during a viral illness like chickenpox. It can lead to liver and brain damage.
Herpes Zoster (Shingles)
Symptoms of Herpes Zoster (Shingles):
- Pain: Shingles are typically characterized by intense pain, often described as burning, tingling, or shooting pain. It may precede the appearance of a rash.
- Rash: The shingles rash appears as a band or cluster of blisters that typically affects one side of the body or face. It follows the path of the affected nerve.
- Itching: The rash can cause itching, which may be severe in some cases.
- Sensory Changes: Some individuals may experience changes in sensation, such as increased sensitivity or numbness, in the affected area.
The complications of shingles can include:
- Postherpetic Neuralgia (PHN): PHN is a common complication of shingles. It refers to persistent nerve pain that lasts for weeks, months, or even years after the rash has healed.
- Vision Problems: If shingles affects the eye (herpes zoster ophthalmicus), it can lead to eye-related complications, including vision loss or corneal damage.
- Secondary Infections: Bacterial infections can occur when the shingles blisters become infected.
It's worth noting that vaccination against VZV has been shown to reduce the severity and complications associated with both chickenpox and shingles. If you suspect you have a VZV infection, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
Shingles, caused by the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus, can bring about significant discomfort and complications, especially for individuals over 50. To combat this, vaccines like Shingrix have emerged as powerful tools for preventing shingles and related complications.
How do I test for Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) infection?
Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) infection can be tested using various laboratory methods. The specific test or combination of tests used depends on the purpose of the testing and the stage of the disease. Here are some common methods used for VZV testing.
One of the most effective ways is by using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test. PCR is a highly sensitive and specific method used to detect the presence of VZV DNA in samples. It can be performed on various specimens, including vesicle fluid, respiratory secretions, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and blood. PCR helps diagnose active VZV infections, including chickenpox and shingles.
What are some of the medical conditions associated with the Varicella-zoster virus (VZV)?
Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) can cause primary and reactivation infections in several medical conditions. Here are the main conditions associated with VZV:
- Chickenpox (Varicella): VZV is the primary infection that causes chickenpox. It is a highly contagious viral illness characterized by a widespread rash of itchy blisters on the skin. Other symptoms may include fever, fatigue, headaches, and body aches. Chickenpox is more common in children but can occur in individuals of any age who have not been previously infected or vaccinated.
- Herpes Zoster (Shingles): Herpes zoster, commonly known as shingles, occurs as a result of the reactivation of VZV from a latent infection. After a person recovers from chickenpox, the virus remains dormant in nerve cells. Factors such as aging, a weakened immune system, or certain medical conditions can reactivate the virus, leading to shingles. Shingles is characterized by a painful rash that usually appears as a single stripe or cluster of blisters on one side of the body. It typically occurs in adults and older individuals.
- Postherpetic Neuralgia (PHN): PHN is a common complication of shingles. It refers to persistent nerve pain that continues even after the shingles rash has healed. PHN can be quite severe and debilitating, affecting the quality of life of individuals. It is more likely to occur in older individuals and can last for months or years.
- Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus (HZO): HZO is a specific form of shingles that affects the eye. The virus affects the ophthalmic branch of the trigeminal nerve, leading to symptoms such as eye pain, redness, a rash on the forehead, eyelids, and around the eye, and sometimes, vision problems. HZO requires prompt medical attention to prevent complications that can affect vision.
- Varicella Pneumonia: In rare cases, VZV can cause pneumonia, particularly in adults or individuals with weakened immune systems. Varicella pneumonia can be severe and may require hospitalization and specific antiviral treatment.
- Congenital Varicella Syndrome: If a pregnant woman develops chickenpox during the first 20 weeks of pregnancy, the virus can potentially infect the fetus. Congenital varicella syndrome can result in various congenital disabilities, including skin scarring, eye abnormalities, limb defects, neurological problems, and growth restriction.
It's important to note that vaccination against VZV has significantly reduced the incidence and severity of these conditions. Vaccination is recommended to prevent chickenpox and reduce the risk of developing shingles later in life.
Prevention and treatment of VZV infections
Vaccination
Prevention and treatment of VZV infections involve several approaches. Vaccination is available to prevent varicella (chickenpox) and shingles. The live attenuated VZV vaccine, Varivax, is recommended for children and has shown effectiveness in preventing varicella infection. Vaccines such as Shingrix have been developed and recommended for adults over a certain age to prevent shingles.
Medication
Antiviral medications like acyclovir, famciclovir, and valaciclovir can be used to treat VZV infections. These drugs can help reduce the severity and duration of symptoms, especially when administered early in the course of the infection. However, intravenous administration is often required for effective treatment.
Trust PULSE CLINIC to take care of your health like other 45000 people from over 130 countries. We provide discreet professional service with high privacy. Here to help, not to judge.
Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) & People Living with HIV
For individuals living with HIV, the Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) can pose unique challenges and risks. Here's some information on how VZV can affect people with HIV:
- Increased risk of severe disease: People with HIV have a higher risk of developing severe or atypical forms of varicella (chickenpox) compared to those with a healthy immune system. This is particularly true for individuals with advanced HIV infection and low CD4 cell counts.
- Higher risk of VZV reactivation: HIV weakens the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to VZV reactivation. Shingles (herpes zoster) is a common manifestation of VZV reactivation. People with HIV are more likely to experience recurrent or disseminated cases of shingles, affecting multiple dermatomes or even involving internal organs.
- Potential for prolonged and severe symptoms: Shingles in people with HIV can be more severe and prolonged compared to individuals with a healthy immune system. The rash and pain associated with shingles may persist for an extended period, leading to significant discomfort and impaired quality of life.
- Increased risk of complications: HIV-infected individuals are at an increased risk of developing complications from VZV infections. These complications can include bacterial superinfection of the skin lesions, pneumonia, encephalitis, or other neurological manifestations.
- Impact on HIV management: VZV infections can have implications for the management of HIV in individuals co-infected with both viruses. VZV reactivation and the associated illness can lead to interruptions in antiretroviral therapy (ART) and pose challenges to maintaining HIV viral suppression.
- Vaccination recommendations: Vaccination against VZV is recommended for individuals living with HIV who are not immune to varicella (chickenpox) or have not had previous VZV infection. The varicella vaccine (Varivax) can be given to eligible individuals with HIV who have a CD4 count of ≥200 cells/mm³ and are not severely immunosuppressed.
It's crucial for people with HIV to work closely with their healthcare providers to manage their HIV infection and take appropriate precautions to prevent VZV infections. Regular HIV care, adherence to ART, and vaccination when indicated can help reduce the risk and severity of VZV-related complications in individuals living with HIV.
PULSE Teleconsult: Connect with Doctors Anytime, Anywhere!
Sometimes you might not be able to go to a STD clinics when you have concerns about your health. PULSE now offers PULSE Telemedicine & Teleconsult, enabling both new and existing patients to connect with doctors from 16 branches across 6 countries during clinic hours for non-emergency consultations. After the consultation, medications are delivered directly to the patient's doorstep.
3 Easy Steps to Get a Teleconsult with PULSE!
- Connect with us Either on Whatsapp, Line App to Chat with us or call us to talk with our staff to request teleconsult
- Verification & Consultation Our team will guide you through the verification process before your online consultation. Our doctors provide virtual consultations via available platforms, just like a traditional visit—only from the comfort of your home! Access care anywhere, anytime.
- Get Your Treatment From Home! If your doctor determines that medication is necessary, they will provide you with a medical certificate and prescription. Your medication can be delivered to your address through our online delivery service, or in some cases, you may choose to use the prescription at a local pharmacy. For certain conditions, further lab tests may be required, and the doctor may recommend scheduling an appointment at one of our clinics near you!
Test of Cure After Treatment with Our Teleconsult Services: Ensuring Complete Recovery
After completing treatment through our teleconsult services, your doctor may recommend a PCR test as a follow-up test of cure. This is to ensure the effectiveness of the treatment and that the prescribed medication has successfully eliminated the infection. We prioritize your health by confirming that no infection remains in your system, helping to prevent persistent or recurrent infections, complications, or the development of drug resistance. Typically, this test is performed around three weeks after your final day of treatment to ensure optimal results.
Teleconsult is now available for booking through our staff at PULSE Clinic. Our team will help guide you through the process to ensure your session with one of our doctors goes as smoothly as possible for you. Contact us at info.bkk@pulse-clinic.com o/ๅr chat on your preferred platform:
![]() +66 65 237 1936
+66 65 237 1936  @PULSEClinic
@PULSEClinic ![]() PulseClinic
PulseClinic
Add us on Line and stay in touch.
Loading...
Clinic Locations
Loading...








